Food shortages due to the global pandemic, geopolitical risks from the Russia-Ukraine war, Houthi attacks on Red Sea shipping, famine, and drought in some African countries heightened food insecurity continent-wide resulting in high inflation and people slipping back into extreme poverty. Although Africa exports billions of tons of agricultural products yearly, it relies heavily on imports to feed its people. Gaps in the agro-processing industry are primarily to blame as raw materials are rarely processed into final goods on the continent. The events of recent years have flipped a switch on the agro-processing industry in Africa and become an industry ripe for investment and development.
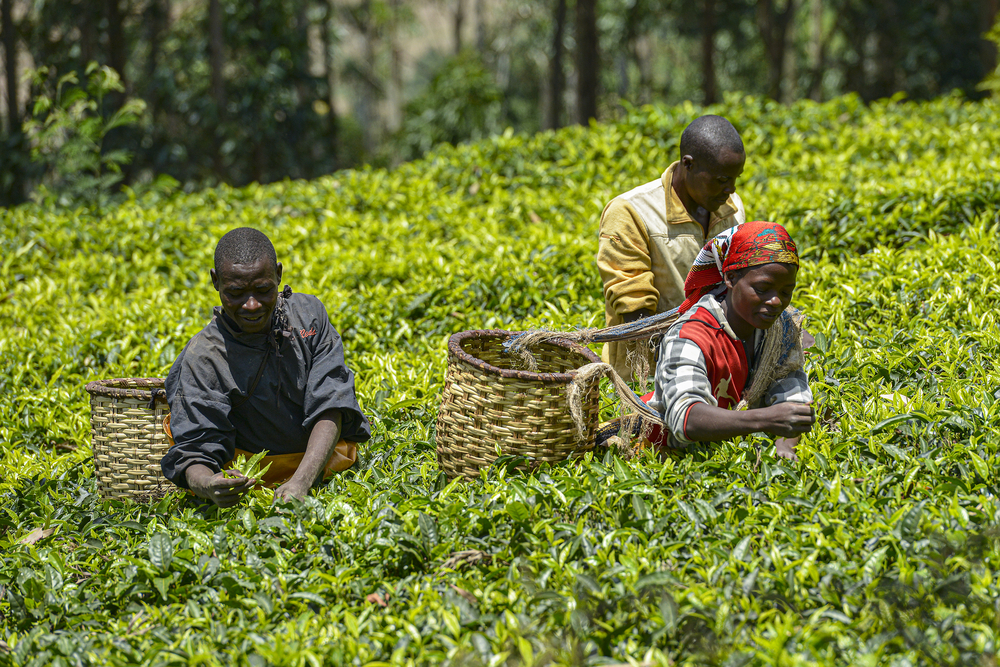
Nearly 23% of Africa’s GDP is from agricultural activities, and over 60% of African households rely on small farms for subsistence. The export of raw agrarian materials is one of the biggest drivers of Africa’s export economy, yet very little of that agricultural material is processed on the continent. This means that Africans sell raw agricultural products to overseas markets, which process the material into final products to be sold around the globe, including back to Africans at a higher price than what they sold the material for.
Adding value chain actors able to process agricultural products in Africa is essential to economic growth. Its exports will fetch a higher price, revenue will be kept locally, and finished food products will be available through the industry on the continent. This will boost local revenue streams and decrease communities’ reliance on imported food products.
This may help to combat the challenges currently facing Africa’s agricultural industry, such as desertification, land degradation, and losses in productivity. Many of these issues result from poverty leading to unsustainable land use and farming practices. Developing the agro-processing industry on the continent may lead to improved land use due to higher household income.
What is holding Africa back from developing its agro-processing industry? One of the biggest obstacles to commercializing the agriculture industry is the lack of adequate infrastructure to support commercial activity. This includes roads, storage facilities, and processing or value chain actors.
Each phase of infrastructure development requires local businesses and governments to access outside financing. This is a potentially lucrative investment as the demand for processed food goods in Africa is set to increase dramatically due to rapid urbanization and establishing regional and continental trading blocs such as the African Continental Free Trade Agreement, which is estimated to boost intra-African trade dramatically.
Another challenge to the agro-processing industry are poorly coordinated markets. For the industry to thrive and reach small-plot farmers, local farmers must access markets and buyers who will store and process their products. This also safeguards yields from after-harvest loss, a significant challenge for African farmers seeking to bring their goods to market. As recently seen in Ghana, investing in commodity exchange services is one way to combat these issues.
As mentioned above, the investment categories necessary for growth in the agro-processing industry are:
Also crucial to the growing agro-processing industry are the other inputs to agri-business, such as machinery and equipment, input supplies, technology, and trade and logistics.
As African states come together with international donors and private investors to enhance the production and processing capabilities of the agricultural industry, the economic impacts will be widespread, especially among impoverished rural communities.
While most of Africa relies heavily on agriculture, several countries will have an outsized impact through their potential for successful agro-processing investments:
It is important to note that each country and sometimes regions within countries have different laws, norms, and risks in the form of unrest, corruption, extortion, and terrorism.
It is essential that general counsels use deep due diligence investigations and risk intelligence to assess transactions before investing in emerging markets such as Africa. Companies seeking to invest in Africa must also navigate a significant amount of risk when doing business in the region. US companies aiming to establish a foothold in emerging markets or seeking out a strategic trade location in Africa should strongly consider putting a due diligence investigations plan in place to assess the basket of risks relevant to a specific investment opportunity. This includes making sure that country-specific risk analysis and geopolitical risk planning takes place before committing significant resources to new ventures.